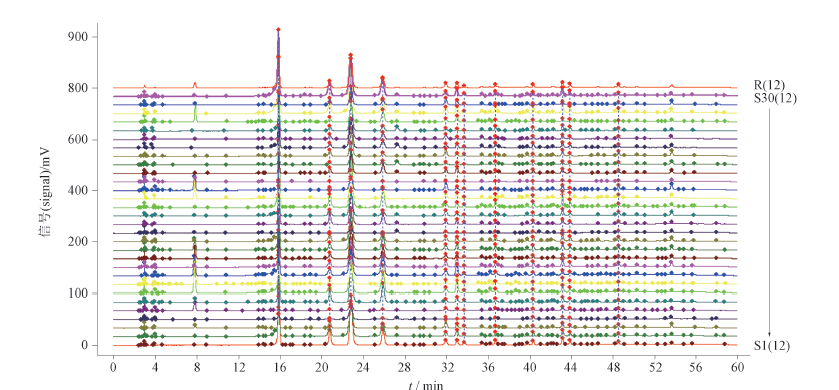
Objective: To evaluate the quality of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium from different habitats and to select the best habitat of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium preferentially based on high performance liquid chromatography fingerprinting and chemical pattern recognition methods. Methods: The detection was performed on an AcclaimTM 120A C18 (250 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm) column with the mobile phase of 0.2% aqueous phosphoric acid (A)-acetonitrile (B) in gradient elution (0-5 min, 5%B; 5-6 min, 5%B→10%B; 6-20 min, 10%B; 20-50 min, 10%B→25%B; 50-60 min, 25%B). The volume flow rate was 1.0 mL·min-1, the detection wavelength was 327 nm, the column temperature was 30 ℃, and the injection volume was 10 μL. The fingerprint profiles of 30 batches of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium from different habitats were established, and the fingerprint profiles combined with chemical pattern recognition were used to conduct comprehensive analysis of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium from different habitats. And cluster analysis(CA), principal component analysis (PCA) and comprehensive scoring were performed on honeyed Eriobotryae Folium from different habitats. Orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA) was used to screen out the differential markers of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium from different habitats, and the habitats of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium were selected based on the comprehensive scoring. Results: The fingerprint profiles of 30 batches of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium were established. Twelve common peaks were identified, and 4 peaks were identified as neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, cryptochlorogenic acid and auriculoside according to the control finger. CA divided the 30 batches of Honeyed Eriobotryae Folium samples into 6 categories. By PCA, 3 principal components were extracted, with a cumulative variance contribution of 84.315%. Six differential markers were obtained according to OPLS-DA, two of which were identified as chrysoside and chlorogenic acid. The better habitats of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium were screened as Sichuan, Guangxi, Guangdong and Shaanxi according to the comprehensive score. Conclusion: Good precision, repeatability and stability results are obtained for fingerprinting and content determination. The combination of fingerprinting and chemical pattern recognition can comprehensively evaluate the quality of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium, and this method is stable and reliable, which can provide an effective reference basis for the habitat study of honeyed Eriobotryae Folium.
[1] 中华人民共和国药典2020年版.一部[S]. 2020:213
ChP 2020.Vol Ⅰ[S]. 2020: 213
[2] 肖旭坤, 王翰华, 阮洪生.枇杷叶化学成分和药理活性研究进展[J]. 中医药导报,2019,25(21):60
XIAO XK, WANG HH, RUAN HS. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Pipaye (Eriobotryae Folium)[J]. Guid J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2019,25 (21): 60
[3] 叶广亿, 李书渊, 陈艳芬, 等.枇杷叶不同提取物的止咳化痰平喘作用比较研究[J]. 中药药理与临床,2013,29(2):100
YE GY, LI SY, CHEN YF, et al. Comparative study of different extracts of loquat leaf in antitussive and expectorant and antiasthmatic effects[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2013,29 (2): 100
[4] 汪世浩, 闫其朋, 周玉波.枇杷叶及其炮制品中总三萜的含量分析[J]. 中国民族民间医药,2017,26(12):22
WANG SH, YAN QP, ZHOU YB. Content determination of total triterpenoids in Folium Eriobotryae processed products[J]. Chin J Ethnomed Ethnopharm, 2017,26 (12): 22
[5] 高伟城,王小平,何丽珊.枇杷叶生品及不同炮制品质量评价[J]. 中国药房,2022,33(2):196
GAO WC, WANG XP, HE LS. Quality evaluation of crude drug and different processed products of Eriobotryae Folium[J]. China Pharm, 2022,33 (2): 196
[6] 李文兵, 许玲, 卢君蓉, 等.基于HPLC指纹图谱的枇杷叶蜜炙前后标准汤剂质量控制研究[J]. 中草药,2020,51(13):3444
LI WB, XU L, LU JR, et al. Quality control study of standard decoction of raw and honey processed Eriobotryae Folium based on HPLC fingerprint[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2020,51 (13):3444
[7] 谢苏梦,季巧遇,吕尚,等.不同产地野菊花HPLC指纹图谱建立及化学模式识别研究[J]. 中草药,2021,52(24):7616
XIE SM, JI QY, LÜ S, et al. Study on establishment of HPLC fingerprints and chemical pattern recognition of Chrysanthemum indicum from different regions[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2021,52 (24): 7616
[8] 位翠杰,陈芳,丁青,等.基于UPLC指纹图谱和多成分定量的茵陈配方颗粒质量控制研究[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志,2021,28(10):99
WEI CJ, CHEN F, DING Q, et al. Quality control of Artemisiae Scopariae Herba dispensing granules based on UPLC fingerprints and multi-component content determination[J]. Chin J Inf Tradit Chin Med, 2021,28 (10): 99
[9] 张泽康,王昌海,赵玥瑛,等.经典名方阳和汤基准样品的HPLC指纹图谱分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(10):13
ZHANG ZK, WANG CH, ZHAO YY, et al. HPLC fingerprint analysis of benchmark sample of Yanghetang[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form,2023,29(10):13
[10] 黄宽,付鹏,林艾和,等.不同产地夏枯草HPLC指纹图谱及化学模式识别研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2021,39(12):124
HUANG K, FU P, LIN AH, et al. Study on HPLC fingerprint and chemical pattern recognition of Xiakucao (Prunella vulgaris) from different producing areas[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2021,39 (12): 124
[11] 陈琳,唐志书,刘妍如,等.UPLC指纹图谱结合化学模式识别评价白芷药材质量[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2019,31(10):1697
CHEN L, TANG ZS, LIU YR, et al. Quality control research of Angelica dahurica base on UPLC fingerprint combined with chemical pattern recognition[J]. Nat Prod Res Dev, 2019,31 (10): 1697
[12] 彭警,樊箫雨,王迪磊,等.基于成分定量和指纹图谱的化学模式识别法评价胆木不同部位的差异性[J]. 中草药,2023,54(10):3281
PENG J,FAN XY,WANG DL, et al.Differences of Nauclea officinalis in different parts based on quantitative analysis of components and fingerprint by chemical pattern recognition[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs,2023,54(10):3281
[13] 张建新,燕雪花,马昕,等.芳香新塔花总黄酮的HPLC指纹图谱研究及化学模式识别分析[J]. 现代中药研究与实践,2021,35(6):45
ZHANG JX, YAN XH, MA X, et al. HPLC fingerprint and chemical pattern recognition of total flavonoids from Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam[J]. Res Pract Chin Med, 2021,35 (6): 45
[14] 童欢,张明伟,张炳武,等.基于指纹图谱、含量测定和化学模式识别的五子衍宗丸质量评价研究[J]. 药物分析杂志,2023,43(1):103
TONG H, ZHANG MW, ZHANG BW, et al. Study on quality evaluation of Wuzi Yanzong pills based on HPLC fingerprint, assay and chemical pattern recognition[J]. Chin J Pharm Anal, 2023,43(1): 103
[15] 赵茜,于佳萍,章聚宝,等.基于高效液相色谱指纹图谱的不同产地不同采摘期昆仑雪菊的化学模式识别及抗氧化谱效关系探究[J]. 理化检验-化学分册,2023,59(2):125
ZHAO Q, YU JP, ZHANG JB, et al. Chemical pattern recognition and antioxidant spectrum-effect relationship development coreopsis tinctoria of Kunlun from different habitats and harvesting periods based on high performance liquid chromatography fingerprint[J]. Phys Test Chem Anal Part B:Chem Anal,2023,59(2): 125
[16] 程茜菲,张玩涛,彭修娟,等.指纹图谱和化学模式识别评价前列舒通胶囊的质量[J]. 华西药学杂志,2023,38(1):95
CHENG QF, ZHANG WT, PENG XJ, et al. Quality evaluation of Qianlie Shutong capsules based on fingerprints and chemical pattern recognition[J]. West China J Pharm Sci, 2023,38 (1): 95


