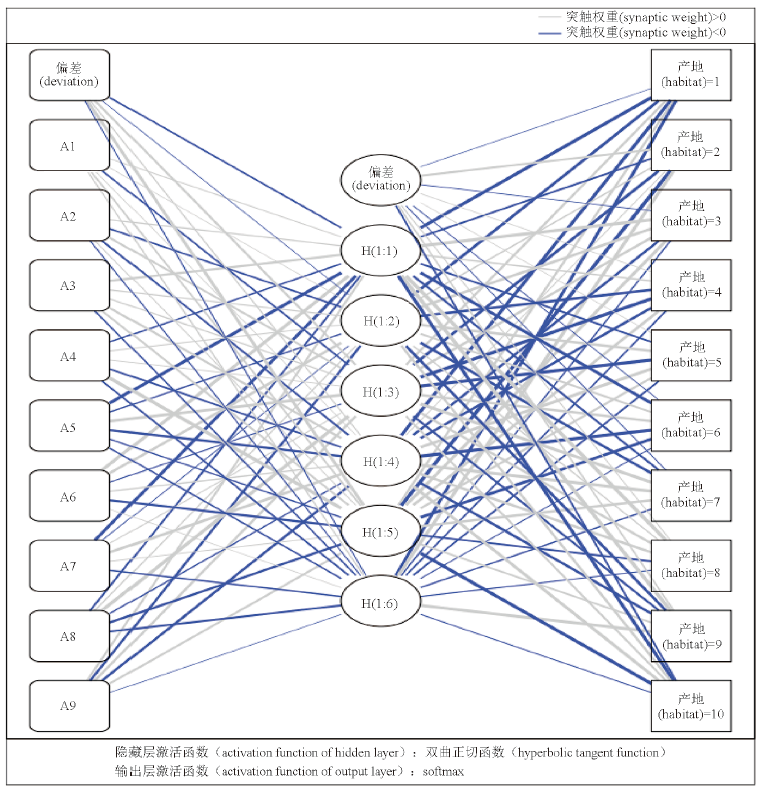
Objective: To establish the UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of 9 components (nicotinic acid, kaempferol, swertisin, quercetin, luteolin, rutin, vitexin, spinosin, salicylic acid) in Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC. and construct a back propagation(BP) neural network model to predict the origin of Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC. from different habitats. Methods: The chromatographic separation was achieved on an Agilent Zorbax SB C18 column (50 mm×3.0 mm,1.8 μm). The mobile phase consisted of methanol-0.1% acctic acid (containing 0.02 mol·L-1 ammonium acetate) at a flow rate of 0.3 mL·min-1 with gradient elution, the MS analysis were performed by multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) under ESI+ and ESI. A correlation analysis was conducted on the contents of each component, and a BP neural network model was constructed to distinguish Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC. from different habitats. Results: Under the optimized conditions, 9 components(nicotinic acid, kaempferol, swertisin, quercetin, luteolin, rutin, vitexin, spinosin, salicylic acid) showed good linear relationships in the ranges of 0.388 8-38.88 ng·mL-1, 10.07-1 006.6 ng·mL-1, 34.22-34 221.6 ng·mL-1, 3.944-394.4 ng·mL-1, 2.124-212.4 ng·mL-1, 4.344-434.4 ng·mL-1, 46.50-4 650.1 ng·mL-1, 1.649-164.9 ng·mL-1, 4.880-488.0 ng·mL-1, respectively (r>0.995 1), whose average recoveries were 96.9%-103.9% (RSDs<1.9%). The contents of the above nine components in 40 batches of Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC. were 1.657-7.407 μg·g-1, 15.801-64.488 μg·g-1, 1 068.348-4 270.780 μg·g-1, 10.608-123.228 μg·g-1, 3.897-16.802 μg·g-1, 1.269-97.834 μg·g-1, 405.285-1 955.796 μg·g-1, 13.614-36.124 μg·g-1, 4.417-87.509 μg·g-1, respectively. According to correlation analysis, four components (swertisin, rutin, spinosin, and luteolin) in Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC. showed a highly linear positive correlation, indicating that these four components had a certain synergistic effect in Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC.. The BP neural network model was constructed to predict Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC. from different habitats, and the accuracy of the test set reached 92.3%. Conclusion: The method is simple, sensitive and efficient, and can be used for the rapid determination of the components in Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC.. Using the BP neural network model to predict the habitats plays a significant role in tracing the origin of Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC..
[1] 张毅, 华琼琼, 孙伊维, 等. 小槐花茎的化学成分的分离与鉴定[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2020, 37(10): 884
ZHANG Y, HUA QQ, SUN YW, et al. Isolation and identification of chemical constituents from the stem of Desmodium caudatum [J]. J Shenyang Pharm Univ, 2020, 37(10): 884
[2] 车鑫, 金成武, 谯明鸣, 等. 小槐花茎叶化学成分的分离与鉴定[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2022, 39(12): 1433
CHE X, JIN CW, QIAO MM, et al. Isolation and identification of chemical constituents from the stem and leaf of Desmodium caudatum [J]. J Shenyang Pharm Univ, 2022, 39(12): 1433
[3] 卢文杰, 陆国寿, 谭晓, 等. 壮瑶药小槐花化学成分研究[J]. 中药材, 2013, 36(12): 1953
LU WJ, LU GS, TAN X, et al. Chemical constituents of Desmodium caudatum[J]. J Chin Med Mater, 2013, 36(12): 1953
[4] 李传宽, 张前军, 黄钟碧, 等. 饿蚂蝗化学成分研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2010, 35(18): 2420
LI CK, ZHANG QJ, HUANG ZB, et al. Chemical constituents of Desmodium sambuense[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2010, 35(18): 2420
[5] PUODZIUNIENE G, KAIRYTE V, JANULIS V, et al. Quantitative HPLC estimation of flavonoids in showy tick trefoil (Desmodium canadense) herbs[J]. Pharm Chem J, 2011, 45(2): 88
[6] 刘超, 吴颖, 张前军, 等. 山蚂蝗属植物化学成分与生物活性研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2013, 38(23): 4006
LIU C, WU Y, ZHANG QJ, et al. Advances in studies on chemical constituents and biological activities of Desmodium species[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2013, 38(23): 4006
[7] 袁见萍, 张前军, 康文艺, 等. 饿蚂蝗中黄酮类化合物的抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 广州化工, 2014, 42(22): 79
YUAN JP, ZHANG QJ, KANG WY, et al. Determination of flavonoids and antioxidant activity of different parts from Desmodium sambuens (DC.)[J]. Guangzhou Chem Ind, 2014, 42(22): 79
[8] 刘舒凌, 吴燕春, 钟振国, 等. 饿蚂蝗总黄酮对鸭乙型肝炎的保护作用研究[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2017, 33(6): 76
LIU SL, WU YC, ZHONG ZG, et al. The effect of total flavonoids from Desmodium multiflorum DC. on DHBV hepatitis[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2017, 33(6): 76
[9] 符传武, 刘永逸, 丘琴, 等. 小槐花的化学成分及质量控制方法研究进展[J]. 中南药学, 2021, 19(6): 1233
FU CW, LIU YY, QIU Q, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and quality control methods of Desmodium caudatum (Thunb.) DC.[J]. Cent South Pharm, 2021, 19(6): 1233
[10] 王虹, 魏秉炎, 王昊云. 基于主成分分析的BP神经网络模型在铁矿产地溯源中的应用[J]. 冶金分析, 2021, 41(9): 11
WANG H, WEI BY, WANG HY, Application of BP neural network model based on principal component analysis in tracing the origin of iron ore[J]. Metall Anal, 2021, 41(9): 11
[11] 彭政, 郭秀芝, 周利, 等. ICP-MS结合化学计量学分析不同来源陈皮中38个无机元素[J]. 中国现代中药, 2021, 23(7): 1204
PENG Z, GUO XZ, ZHOU L, et al. Quantitative analysis of 39 inorganic elements in Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from different sources by ICP-MS combined with chemometrics[J]. Mod Chin Med, 2021, 23(7): 1204
[12] 柴海华. 基于BP神经网络的兰州新区现代有轨电车适用性评价[J]. 时代汽车, 2023(22): 25
CHAI HH. Applicability evaluation of modern trams in Lanzhou new district based on BP neural network[J]. Auto Time, 2023(22): 25
[13] 周梦, 吕志刚, 邸若海, 等. 基于小样本数据的BP神经网络建模[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(7): 2754
ZHOU M, LÜ ZG, DI RH. BP neural network modeling based on small sample data[J]. Sci Technol Eng, 2022, 22(7): 2754
[14] 姚冲, 钱晓东, 李丽琴, 等. ATR-FTIR结合RBF神经网络对市售西红花的产地溯源[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2019, 37(6): 1323
YAO C, QIAN XD, LI LQ, et al. Geographical traceability of traded saffron (Crocus sativus L.) by ATR-FTIR and RBF neural network[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2019, 37(6): 1323
[15] 曹爱华, 秦鹏, 李爽. FTIR法结合ANNs鉴别普洱茶的产地和年限[J]. 中国城乡企业卫生, 2018, 33(10): 175
CAO AH, QIN P, LI S. Identification of the origin and age of Pu'er tea by FTIR combined with ANNs[J]. Chin J Urban Rural Enterpr Hyg, 2018, 33(10): 175
[16] 朱志均, 周华英, 罗坤豪, 等. 基于机器嗅觉结合BP神经网络的砂仁气味鉴别方法[J]. 自动化与信息工程, 2018, 39(4): 45
ZHU ZJ, ZHOU HY, LUO KH, et al. Odor identification of Aromi Fructus based on machine olfactory combined with BP neural network[J]. Autom Inf Eng, 2018, 39(4): 45


