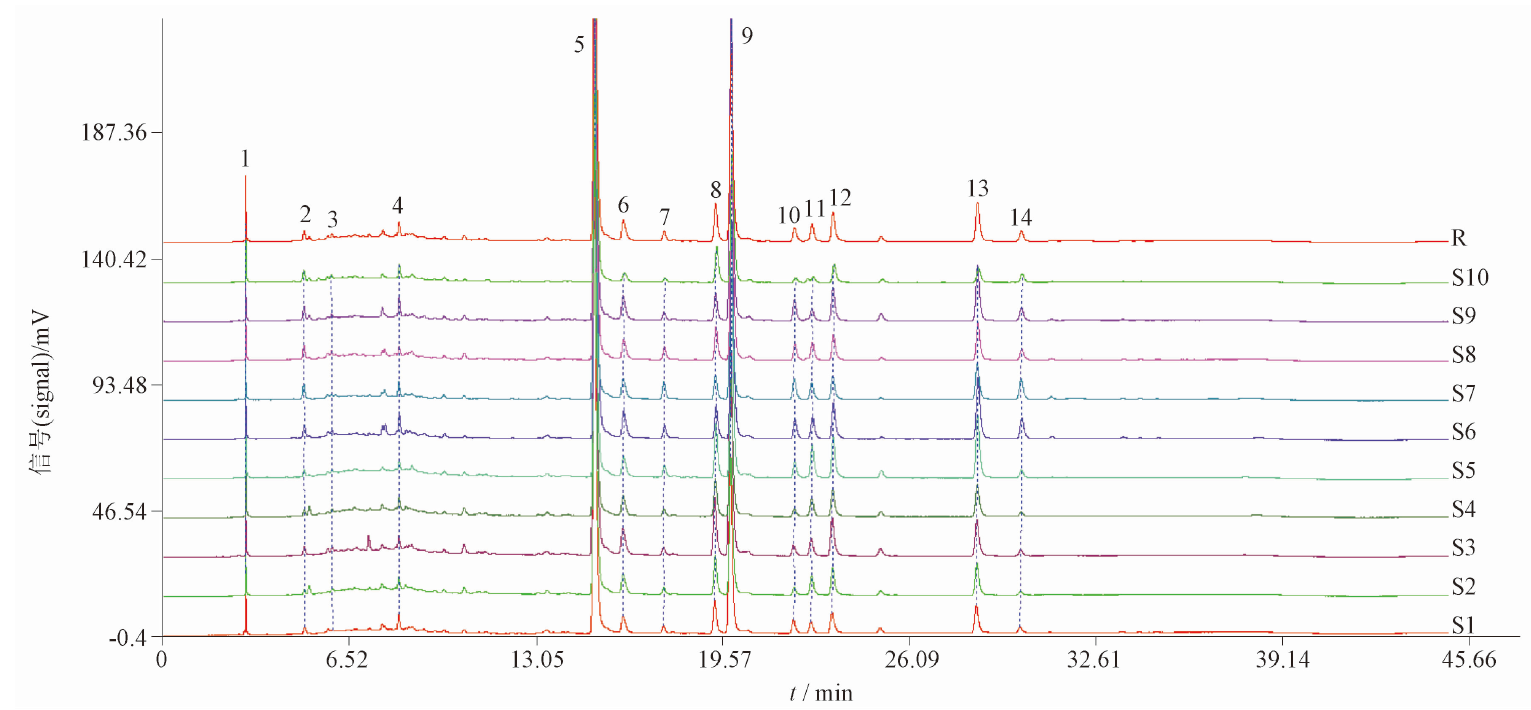
目的:基于指纹图谱、多成分定量及化学模式识别法结合的方法,评价不同产地杉木叶质量,为其深入开发利用提供依据。方法:采用HPLC法测定杉木叶中穗花杉双黄酮、7-去甲基银杏双黄酮、扁柏双黄酮、银杏双黄酮、异银杏双黄酮、金松双黄酮的含量;建立10批不同产地杉木叶指纹图谱;基于指纹图谱共有峰峰面积结果,采用主成分分析(PCA)、正交偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA)、统计学分析、模式识别的化学计量学方法评价杉木叶整体质量。结果:10批杉木叶共确定14个共有峰,相似度范围为0.955~1.000,具有较好的一致性;样品中穗花杉双黄酮、7-去甲基银杏双黄酮、扁柏双黄酮、银杏双黄酮、异银杏双黄酮、金松双黄酮6个双黄酮成分的质量分数分别为2.42~5.24、0.10~0.24、1.55~3.67、0.21~0.89、0.10~0.24、0.51~2.39 mg·g-1;通过PCA,进一步评价不同产地间杉木叶质量差异,将10批药材分为三大类,得到4个影响杉木叶分类的主要因子,最后采用OPLS-DA筛选出色谱峰6、12、7(7-去甲基银杏双黄酮)、13(金松双黄酮)、5(穗花杉双黄酮)、9(扁柏双黄酮)、2等7个差异标志物,可用于区分不同批次杉木叶。结论:建立的杉木叶质量评价方法稳定,结果可信,结合化学模式识别可用于杉木叶药材的质量品质评价。
Objective: To base on the method of HPLC fingerprint, multi-component quantification and chemical pattern recognition, to evaluate the quality of leaves of Cunninghamia lanceolata from different producing areas and to provide basis for further development and utilization. Methods: High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to determine the contents of amentoflavone, bilobetin, hinokiflavone, ginkgetin, isoginkgetin and sciadopitysin in the Cunninghamia lanceolata. Fingerprints of 10 batches of Cunninghamia lanceolata from different habitats were established. Based on the common peak area of the fingerprint, the overall quality of Cunninghamia lanceolata was evaluated by principal component analysis(PCA), orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA), statistical analysis, and pattern recognition chemometrics methods. Results: A total of 14 common peaks in 10 batches of leaves of Cunninghamia lanceolata, and the similarity ranged from 0.955 to 1.000 with good consistency. The mass fractions of six biflavones in the sample were 2.42-5.24 mg·g-1, 0.10-0.24 mg·g-1, 1.55-3.67 mg·g-1, 0.21-0.89 mg·g-1, 0.10-0.24 mg·g-1 and 0.51-2.39 mg·g-1, respectively, including amentoflavone, bilobetin, hinokiflavone, ginkgetin, isoginkgetin and sciadopitysin. According PCA, the difference in the quality of Cunninghamia lanceolata from different habitats was further evaluated. Ten batches of medicinal materials were divided into three major categories, and four main factors affecting the classification of Cunninghamia lanceolata were found. Finally, OPLS-DA screened the excellent spectral peaks 6, 12, 7 (7-demethylated ginkgo biloba biflavone), 13 (kumatsu biflavone), 5 (Amentotaxus argotaenia biflavone), 9 (chamaecypress biflavone) and 2, etc, seven differential markers can be used to distinguish different batches of Cunninghamia lanceolata. Conclusion: The established method is simple to stable and reliable. Combined with chemical pattern recognition, it can be used for the quality evaluation of Cunninghamia lanceolata.
[1] 国家中医药管理局《中华本草》编委会. 中华本草:第二册[M]. 上海:上海科学技术出版社,1999:315
National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Editorial Board of Chinese Materia Medica. Chinese Materia Medica. Vol Ⅱ [M]. Shanghai:Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 1999:315
[2] 广西中药材标准[S]. 1996:119
Medicinal Materials Standards of Guangxi [S]. 1996:119
[3] 广西壮族自治区药品监督管理局. 广西壮族自治区药品监督管理局关于广西壮族自治区瑶药材质量标准(第二卷)的公示[EB/OL]. (2021-12-06)[2022-12-14] http://yjj.gxzf.gov.cn/yp/ypgzwj/t10910167.shtml
Drug Administration of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Public Notice about the Quality Standard of Yao Medicine in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Volume II) from Drug Administration of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region [EB/OL]. (2021-12-06)[2022-12-14] http://yjj.gxzf.gov.cn/yp/ypgzwj/t10910167.shtml
[4] 刘娟,张曼. 杉木化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2010, 12(9):8
LIU J, ZHANG M. Research on chemical constituents and pharmacological activity of Cunninghamia lanceolata [J]. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2010, 12(9):8
[5] 张曼,刘进鹏,刘娟,等. 不同产地杉木枝叶中穗花杉双黄酮的含量测定[J]. 药学服务与研究,2011, 11(2):149
ZHANG M, LIU JP, LIU J, et al. Determination of amentoflavone in Cunninghamia lanceolata from different habitats [J]. Pharm Care Res, 2011, 11(2):149
[6] 刘进鹏,吴纯洁,辛海量,等. 星点设计-效应面法优化杉木枝叶中双黄酮的提取工艺[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2012, 24(4):514
LIU JP, WU CJ, XIN HL, et al. Optimum extracting process for biflavone of the leaves and branches of Cunninghamia lanceolata by central composite [J]. Nat Prod Res Dev, 2012, 24(4):514
[7] 谢培山. 色谱指纹图谱分析是中草药质量控制的可行策略[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2001, 12(3):141
XIE PS. Chromatographic fingerprint analysis is a feasible strategy for quality control of Chinese herbal medicine [J]. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol [J]. 2001,12(3):141
[8] 黄建猷,胡筱希,麦琬婷,等. 指纹图谱及多成分定量结合化学模式识别法评价不同产地消瘤藤质量[J]. 中草药,2021, 52(14):4334
HUANG JY, HU XX, MAI WT, et al. Quality evaluation of Pileostegia tomentella from different habitats by fingerprint and multi-component quantification combined with chemical pattern recognition [J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2021, 52(14):4334
[9] 乔亚玲,刘亚蓉,张春平,等. 基于UPLC指纹图谱、含量测定及化学识别模式的藏药多腺悬钩子质量评价研究[J]. 药物分析杂志,2023, 43(1):85
QIAO YL, LIU YR, ZHANG CP, et al. Quality evaluation of Tibetan medicine Rubus phoenicolasius Maxim. based on UPLC fingerprint, content determination and chemical pattern recognition analysis [J]. Chin J Pharm Anal, 2023, 43(1):85
[10] 徐智,束俭辉,谭桂山. 双黄酮类化合物研究进展[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2004, 14(7):88
XU Z, SHU JH, TAN GS. Research progress of bis-flavonoid [J]. Chin J Mod Med, 2004, 14(7):88
[11] 王曜晖,赵智权,杜运松,等. 穗花杉双黄酮对3T3-L1细胞增殖、凋亡及生物钟的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2019, 29(16):1
WANG YH, ZHAO ZQ, DU YS, et al. Effects of amentoflavone on proliferation, apoptosis and circadian clock of 3T3-L1 cells [J]. Chin J Mod Med, 2019, 29(16):1
[12] 王刚,才谦,李三华,等. 石上柏双黄酮类和酚酸类成分体外抗氧化和抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2018, 20(7):5
WANG G, CAI Q, LI SH, et al. Study on antioxidant and antitumor activity of bioflavonoids and phenolic acids from Selaginella doederleinii in vitro [J]. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2018, 20(7):5
[13] 涂清波,孙云,许婷,等. 银杏双黄酮药理作用的研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2018, 58(19):112
TU QB, SUN Y, XU T, et al. The research progress on pharmacological action of ginkgetin [J]. Shandong Med J, 2018,58(19):112
[14] 刘进鹏. 杉木枝叶黄酮类成分抗骨质疏松研究[D]. 成都:成都中医药大学, 2011
LIU JP. The Anti-osteoporosis Sctivity of Flavonoids from Branches of Cunninghamia lanceolata [D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011
[15] 张曼,刘娟,刘品,等. 杉木枝叶的化学成分[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版),2011,29(5):67
ZHANG M, LIU J, LIU P, et al. Study on chemical constituents of the branches and leaves of Cunninghamia lanceolata [J]. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Agric Sci), 2011,29(5):67



