
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, All Rights Reserved.
E-mail:ywfx@nifdc.org.cn
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd.
[Editor’s Note]
Stem cells are a class of primitive, undifferentiated cells characterized by their capacity for self-renewal, intrinsic homing capability, low immunogenicity, multipotent differentiation potential, and the ability to regenerate various tissues and organs. These unique biological properties make them a promising therapeutic tool for numerous intractable and severe human diseases. Over the years, the significant global attention has been directed toward advancing stem cells research and clinical translation, with the publication of a series of guidelines to facilitate their clinical application. In 2008, the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) published the Guidelines for the Clinical Translation of Stem Cells. In 2009, the International Stem Cell Forum (ISCF) released the Guidelines for the Derivation and Distribution of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Lines, which provided foundational standards for the translational development of stem cell-based therapies. Subsequently, regulatory agencies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), the World Health Organization (WHO), the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), ISSCR, and ISCF, have developed technical specification and updated technical guidelines. These guidelines encompass quality control from the procurement of raw materials to the final product, as well as preclinical and clinical studies. As of October 23, 2024, a keyword search for “stem cell” on ClinicalTrials.gov identified 13 021 globally registered clinical trials focused on stem cell-based therapies, including 1 942 studies with published results. To date, over 20 stem cell-based pharmaceutical products have been approved for market worldwide. Stem cell therapy has thus emerged as a critical focus in international biomedical research, driving innovation and advancing the frontiers of regenerative medicine.
In our country, the National Health and Family Planning Commission and the China Food and Drug Administration jointly issued the Administrative Measures for Stem Cell Clinical Research (Trial) on July 20, 2015. Shortly thereafter, on July 31, 2015, the two agencies collaboratively formulated the Guidelines for Quality Control of Stem Cell Preparations and Preclinical Research (Trial) to ensure the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapies. In recent years, the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) of the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has released a series of relevant technical guidelines, including: Technical Guidelines for Research and Evaluation of Cell Therapy Products (Trial) (December 2017), Technical Guidelines for Pharmaceutical Research and Evaluation of Human Stem Cell Products (Trial) (April 2023), and Technical Guidelines for Nonclinical Research of Human Stem Cell Products (Trial) (January 2024). As of the end of December 2024, a total of 159 stem cell pharmaceutical products have submitted IND applications to the NMPA. Among these, 72 products have been granted clinical trial approval by default. The indications for these therapies include pulmonary fibrosis, knee osteoarthritis, bone fractures, liver cirrhosis, acute-on-chronic liver failure, stroke, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic foot ulcers, Crohn’s disease, and others.Crohn's disease, and others. On January 2nd, 2025, China's first stem cell therapy drug, Amy Metotrexate Injection (trade name: Ruibo Sheng), was approved for marketing, marking a new stage in China's stem cell therapy field.
Compared with other pharmaceuticals, stem cells possess self-renewal and multipotent differentiation capabilities. As a result, stem cell products exhibit diverse cell types, with the cells themselves capable of in vivo survival, proliferation, differentiation, and intercellular interactions. As living, sterile injectable medicines, stem cell products are exposed to significant variability in aspects such as cell source, type, expansion, genetic modification, and induced differentiation during production. This inherent heterogeneity and instability result in relatively short usage windows and present challenges in ensuring consistent quality. Consequently, quality control for stem cell products is more complicated, necessitating the development of novel, rapid, and effective testing methodologies and technologies. To tackle these challenges, we applied for and undertook part of the CGT (Cell and Gene Therapy) research project funded by the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission. The project, titled Key Technologies for Quality Control and Service Platform Construction for Genetically Modified Immune Cells and Gene Therapy Drugs, includes the development of innovative testing methods for stem cell products. These advancements lay a foundation for enterprises to conduct testing required for clinical research applications or new drug approvals for stem cell products.
To embrace the forthcoming boom in stem cell product research, we have organized a team of stem cell product quality analysis experts to author several specialized articles. These contributions form a three-part series titled Special Column on Quality Research and Evaluation of Stem Cell Products. The series covers novel techniques and methods for quality control and testing of stem cell products, as well as the establishment of quality systems for stem cell testing laboratories. This issue features four articles, including: “Research Progress on Quality Control Analysis Methods for Stem Cell Products” “Biological Activity Methods Development of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Products” “Establishment of RT-qPCR Method for Telomerase Catalytic Subunits of Mesenchymal Stem Cells” and “The Construction of AAV Vector-HPV16-HPV18-HPyV Pseudoviruses and Application in the Examination of Human-derived Viruses in Stem Cells”. We hope the insights shared in this column will serve valuable opinions for relevant enterprises and research institutions, accelerating the clinical research and industrialization of stem cell products.
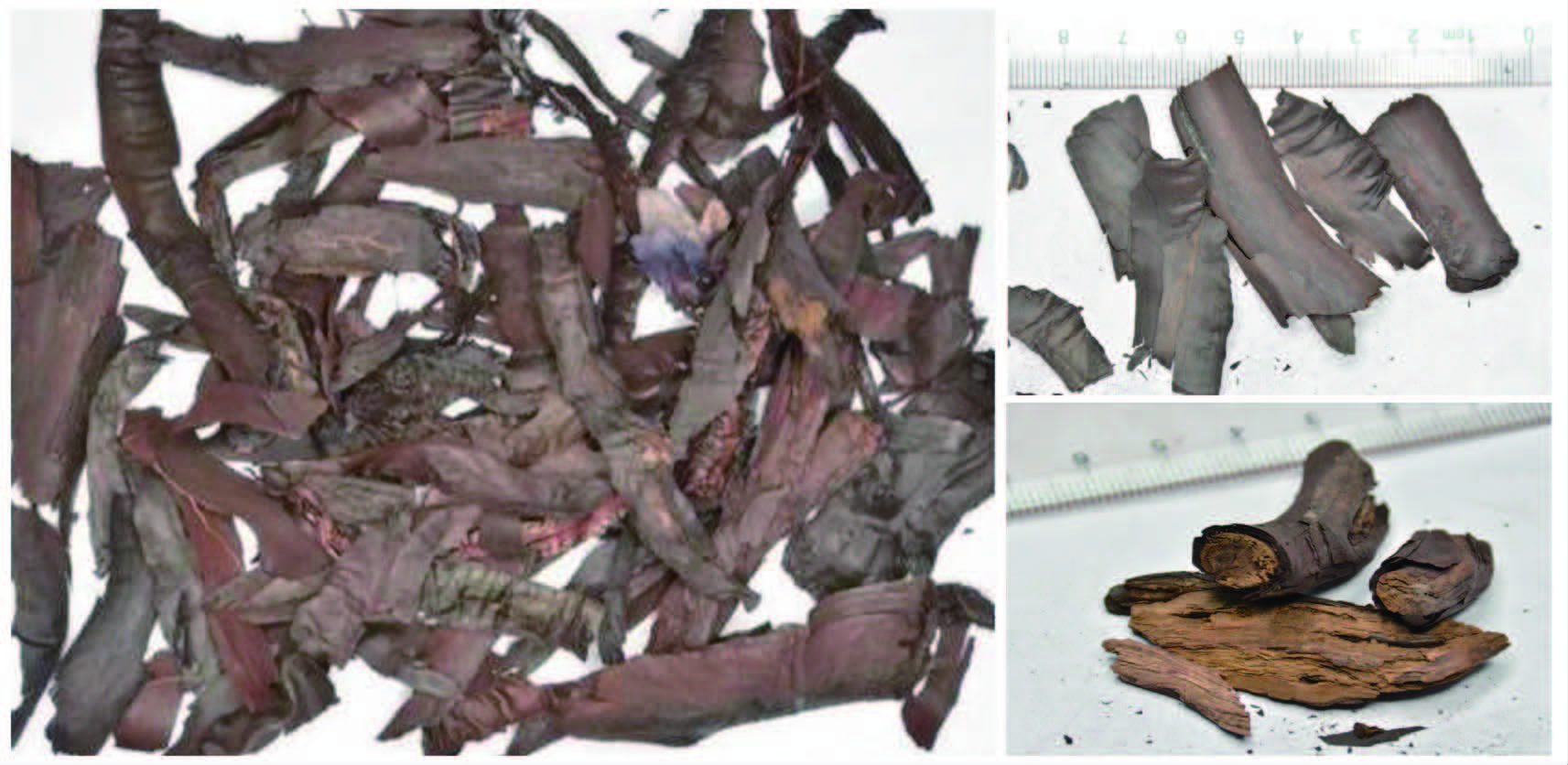

Arnebiae Radix is a common medicinal herb used in ethnic minority areas, and is also a commonly used bulk Chinese medicine. At present, the annual demand for the domestic Chinese herbal medicine market is about 1,200 tons, but the annual output of Arnebiae Radix is less than 100 tons. Arnebiae Radix functions as clear heat, cool the blood, activate blood, remove toxin, promote eruption and resolve macule, and can be used for exuberant blood heat-toxin, manifested as dark purple macule and papule, unerupted measles, sore and ulcer, eczema, scald and burn. There are 122 Chinese patent medicine prescriptions and 195 Chinese medicine formulas containing Arnebiae Radix, indicating that Arnebiae Radix is widely used and has important medicinal value. In addition to Arnebia guttata Bunge and Arnebiae Radix adopted by the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (ChP), other species of Arnebiae Radix are common in the market. Lithospermum erythrorhizon is used in Hebei, Liaoning, and Jiangxi, among others. In Yunnan and other places, it is common to use Onosma paniculatum and Onosma exsertum Hemsl. In Sichuan and other places, it is common to use Onosma confertum. Potentilla chinensis Ser.(Commonly known as Northern Arnebiae Radix)of the Rosaceae family is commonly used in Guangxi and Guangdong. The insufficient supply of the species adopted by ChP and the inconsistent species used in local, and the imported species (the exact species are not yet clear) in the market lead to confused application of Arnebiae Radix. Currently, Arnebiae Radix, one of the species adopted by ChP, has been artificially cultivated. But the consistency between cultivated Arnebiae Radix and wild Arnebiae Radix needs to be examined. Therefore, it is a very important and urgent task to expand the resources of Arnebiae Radix to fill the gap of market demand.
In 2015, Institute for Control of Chinese Traditional Medicine and Ethnic Medicine, National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, carried out a national sampling of Arnebiae Radix. It was concluded that the resource of Arnebiae Radix were scarce, and that of Arnebia guttata Bunge was on the verge of depletion in Inner Mongolia. Besides, a considerable proportion of Arnebiae Radix prepared slices from the market were unqualified. Therefore, the Institute for Control of Chinese Traditional Medicine and Ethnic Medicine initiated special research on Boraginaceous herbs and assisted in the cultivation of Arnebiae Radix. Now the herb has been successfully cultivated in many parts of the country and continues to expand its cultivation area, intending to solve the problem of the scarcity of resources for Arnebiae Radix. In 2022, the Institute for Control of Chinese Traditional Medicine and Ethnic Medicine performed the national drug sampling of Arnebiae Radix again, and the results showed that the qualification rate of Arnebiae Radix prepared slices increased from 43.9% in 2015 to 87.5%, a substantial increase in qualification rate.
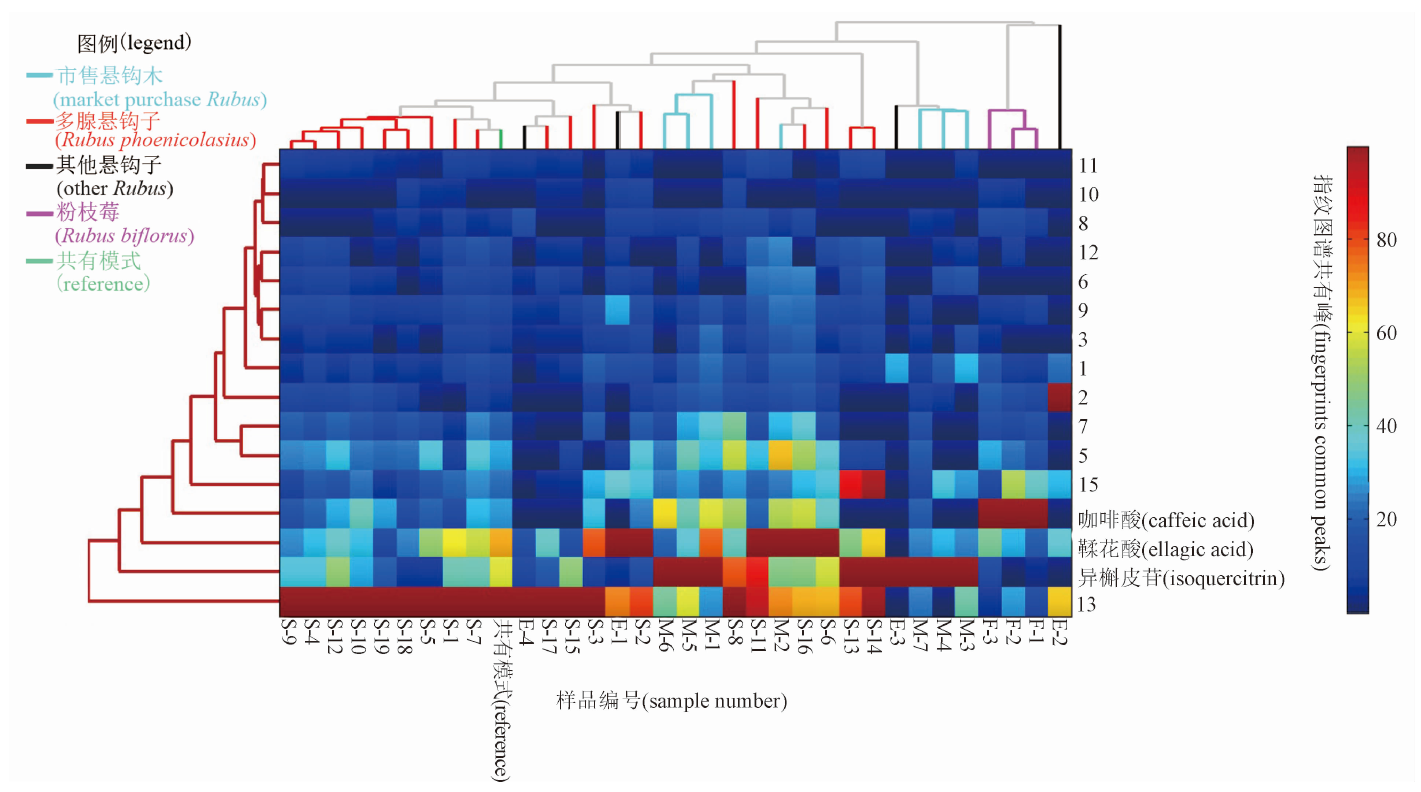
In order to carry out in-depth research on the quality standard of Arnebiae Radix, this journal specializes in “Column on Quality Evaluation of Arnebiae Radix”. “Discussion on the quality status of Arnebiae Radix based on the national drug sampling and testing in 2015 and 2022” comprehensively analyzed the problems reflected in the two sampling tests of Arnebiae Radix. The results indicated that it was of great significance to improve the standards of the ChP of Arnebiae Radix, to establish scientific test items and to strengthen the construction of the quality control system for the supervision of Arnebiae Radix. “The ITS2 sequences’ characters study of imported Arnebiae Radix based on DNA barcoding and PCR-RFLP technologies” provided reference basis for quality control and authenticity identification of marketed Arnebiae Radix and its prepared slices. “The screening of identification primers for Arnebiae Radix based on nested PCR” could be used to efficiently amplify and identify the specific primers for the authenticity of Arnebiae Radix market samples, which provided a referable basis for the subsequent research and development of the identification methods of Arnebiae Radix.“Study on quality control of Arnebiae Radix based on ‘color discrimination grading’ ” compared the correlation between the color of Arnebiae Radix and the contents of six major purple pigment components, and evaluated the quality of Arnebiae Radix by the color of herbs. “The comparative study on the regulation effect of authentic and counterfeit Arnebiae Radix on intestinal flora in mice” compared the similarities and differences in the regulatory effects of authentic and counterfeit products of Arnebiae Radix market herbs on the intestinal flora of mice, relying on the method of macrogenomic sequencing. “Comparative study on the quality of wild and cultivated Arnebiae Radix” conducted a comparative study of the quality of wild and cultivated Arnebiae Radix by using trait comparisons and chemometrics to compare the dissimilar components of wild and cultivated Arnebiae Radix with those of cultivated products from three different regions to establish the optimal Arnebiae Radix cultivation site.
Through this research column, the journal hopes to provide new ideas and methods for Arnebiae Radix research, on the basis of which the depth and breadth of Arnebiae Radix research can be expanded, thus promoting the innovative development of Arnebiae Radix.
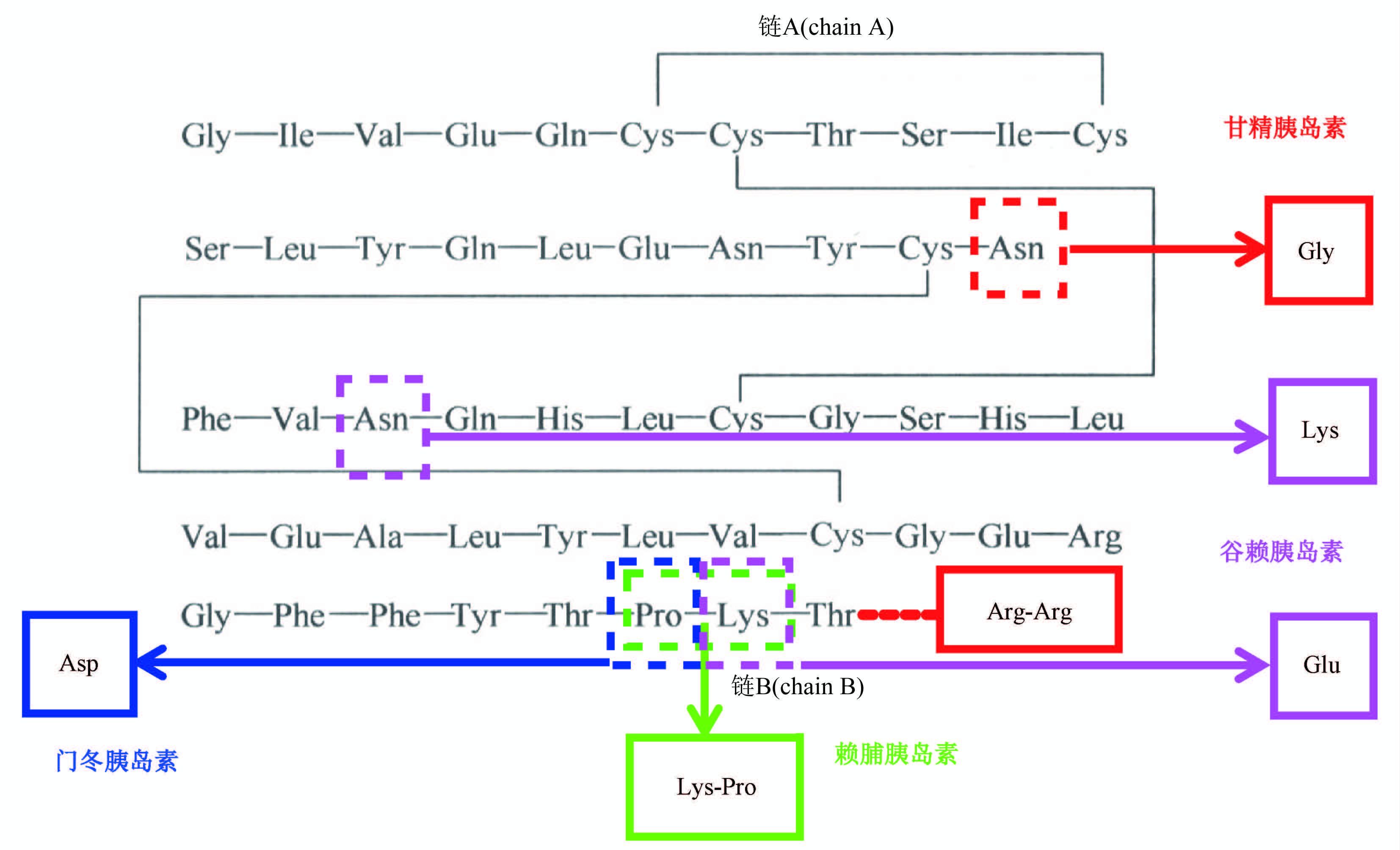
Recombinant hormones are pioneers among biotechnology products for clinical treatment, and their total global sales volume second only to monoclonal antibodies in current biotherapeutic proteins market. They played an irreplaceable role in clinical treatment of various chronic diseases and degenerative diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, reproductive diseases, and osteoporosis. Therefore, they are of great significance to national medical insurance, public health and other livelihood projects. Since the design basis of recombinant hormone drugs mainly comes from the active molecules of proteins and polypeptide naturally existing in human and animals bodies, after more than 100 years of research, human beings have established a comprehensive understanding of their molecular category, pharmacology and efficacy. Therefore, it is very difficult to develop innovative drugs based on the source of new targets and new molecular entities presently. International research and development hotspots mainly focus on long-acting, protein engineering modification and compound preparation products with great clinical value, such as insulin glargine, insulin lispro, insulin degludec, liraglutide and dulaglutide are all "blockbuster" biological drugs. Due to the large population base and gradually emerged aging problem in our country, the clinical demand for recombinant hormone drugs is still in the stage of rapid growth. Numbers of approved domestic products and relative manufacturers have increased significantly in recent years. Some clinical urgently needed new recombinant hormones, which still rely on imports, have already been submitted to the process of license.
With the development of biotechnology industry and the persistent support of the national drug regulatory agency, National Institutes for Food and Drug Control (NIFDC) has accumulated rich experience in the research of quality control analytic methods and quality standards of recombinant hormone drugs. Consequently, such monographs recorded in the national pharmacopoeia continue to maintain the international level. In addition, based on a number of creative studies carried out by NIFDC in polyethylene glycol modified recombinant hormone drugs, the first general monograph for “pegylated recombinant protein and polypeptide products for human use” in the world was successfully recorded in Volume Ⅲ of Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020.
Due to the needs of development, the monographs of recombinant hormones were transferred to Volume Ⅲ since 2020. To achieve the goals, NIFDC undertook a series of standard improvement projects of the National Pharmacopoeia Committee. As a result, 10 monographs, including human insulin and its preparations, insulin glargine and its preparations, insulin lispro and its preparations, and human growth hormone for injection, were deliberately drafted or revised.
This special column includes 10 papers which written by relevant professionals of NIFDC. The content involves the strategy and technical considerations of the national standard research of recombinant hormone drugs, targeted research works carried out in the process of standard improvement, exploratory studies on in vitro bioassay methods aimed to method replacement, and the development of national reference substance. The purpose is to provide reference for how to make the national standard of recombinant hormone drugs further meet the strategic needs of supporting regulation, promoting industry development and international mutual recognition. Meanwhile, we hope that this special column may provide some inspiring ideas for the quality design and R & D decision-making in the development of recombinant hormone products and may help native listed products to enhance the global value.
Gene therapy refers to the method of treating diseases by introducing nucleic acid fragments into cells in an appropriate manner, allowing the genetic information of nucleic acids to function accordingly. Gene therapy products are tools for implementing this method.
Since the 1990s, gene therapy has developed rapidly. In this century, a number of gene therapy products at home and abroad have been approved for marketing. Among them, seven varieties of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vector gene therapy products have been approved for marketing worldwide. In the past three years, 26 rAAV products have been approved for clinical trials at home, with indications including ophthalmic diseases, blood system diseases, nervous system diseases and infectious diseases, and serotypes involving 2type, 5type, 8type, 9type and 10type.
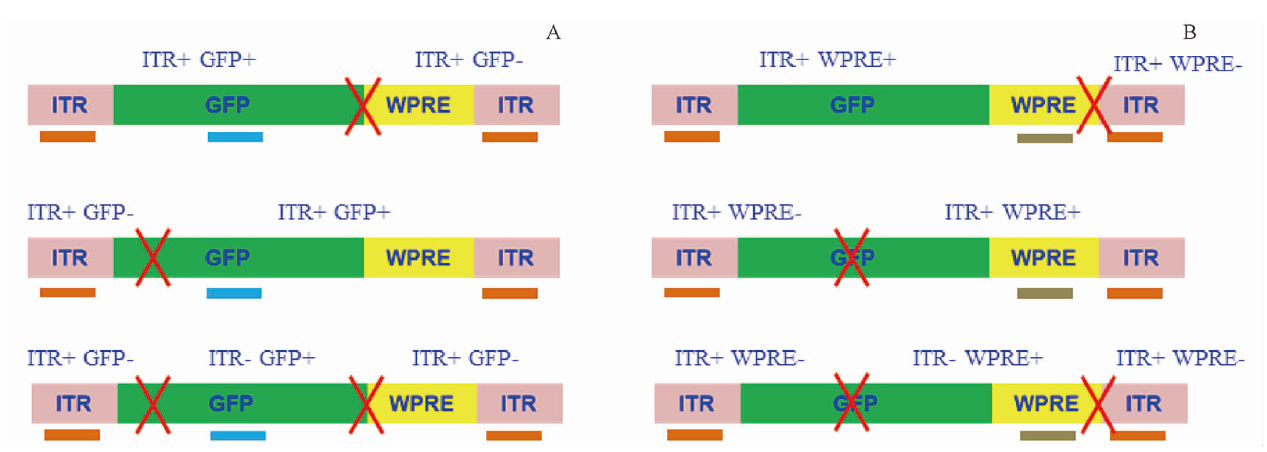
As more and more gene therapy products enter clinical practice, potential safety risks are gradually being exposed. Therefore, regulatory authorities in various countries are accelerating the development of relevant regulations and technical guidelines to guide the research and evaluation of gene therapy products. The 2020 edition Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China, Parts Ⅲ, “General Introduction to Human Gene Therapy Products” and the relevant guiding principles for rAAV gene therapy products issued by the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) of the National Medical Products Administration, which have put forward principle requirements for quality control. However, given that rAAV is a “live” form of virus, its higher requirements for production and quality control and the current testing method continuously improving are still required, including the durability of the method and the repeatability of the results. Therefore, in order to promote the early application of new concepts, technologies, tools, and standards in the quality control of gene therapy products, a “Gene Therapy Product Quality Evaluation Technology and Methods Column” has been specially established to showcase relevant research progress of quality analysis technology. The column includes 9 articles published in 2 journals. Five papers were published in 2023(11), the others published in column(2) of the jounal with following key contents: 1.Exploration and application of multiple digital PCR in rAAV genome integrity evaluation, explores the quantitative methods for the complete genome of rAAV products. 2.Detection of plasmid DNA residues in rAAV products by digital PCR technology, explores a method of characterizing residue by plasmid DNA copy number. 3.Detection of replication-competent AAV(rcAAV) in rAAV2-ND4 injection by qPCR, explores a method for detecting rcAAV through 2-round culture and qPCR. 4.Sequence analysis of amino acid residues in adeno-associated virus capsid protein of different serotypes, explores the principle of serotypes changes in rAAV products.
It’s hoped to use the columns to attract the attention of relevant enterprises and research institutions to the quality of rAAV products, continuously to improve the understanding of practitioners in the dimension of rAAV product quality control, to improve inspection and testing capabilities, and to explore and establish corresponding experimental plans to promote the resolution of difficult problems, thereby promoting the construction of China's rAAV gene therapy product quality control system and the improvement of technical specifications, and accelerating the realization of the grand goal of becoming a pharmaceutical powerhouse.
Gene therapy in a broad sense refers to the introduction of nucleic acid fragments into cells in an appropriate manner, enabling the genetic information of nucleic acid sequences to perform corresponding functions and achieve the goal of treating diseases.
Since the 1990s, gene therapy has developed rapidly. In this century, a number of gene therapy products at home and abroad have been approved for marketing, of which seven varieties of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vector gene therapy products have been approved for marketing worldwide. In recent three years, 26 rAAV products have been approved for clinical trials, with indications including eye diseases, blood system diseases, nervous system diseases and infectious diseases, serotypes involving type 2, 5, 8, 9, and 10.
As more and more gene therapy products enter clinical practice, potential safety risks are gradually exposed. Therefore, regulatory authorities in various countries are also accelerating the development of relevant regulations and technical guidelines to guide the research and evaluation of gene therapy products. The 2020 edition of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, Part Three “General Introduction to Human Gene Therapy Products”, and the relevant guiding principles for rAAV gene therapy products issued by the Drug Evaluation Center (CDE) of the National Drug Administration have put forward principled requirements for quality control. However, as rAAV is a “live” virus, its production and quality control require higher requirements, and the current testing methods still need to be continuously improved, the durability of the method and the repeatability of the results also need to be improved. Therefore, in order to promote the early application of new concepts, technologies, tools, and standards in the quality control of gene therapy products, a “Column on Quality Evaluation Techniques and Methods for Gene Therapy Products” has been specially established to showcase the relevant research progress of quality analysis technology. The column includes 9 articles, which are divided into 2 issues due to their long length. The topics and focus of this issue includes: ①Critical considerations for quality control testing technology of recombinant adeno-associated virus(rAAV)gene therapy products, which introduces the exclusive testing project settings and method specific inspection points for rAAV products. ②Biological activity detection method for gene transcription level of rAAV2-ND4 injection, focuses on introducing a biological activity detection method with dual calibration of internal reference genes and reference substances. ③Study on digital PCR methods for rAAV5 genomic titer determination, which focuses on the comparison between micro droplets and chip digital PCR. ④Analysis of the proportion content of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) capsid protein by CGE-LIF, which describes the detection method for relative quantification of capsid protein subunits using CE-LIF technology. ⑤Analysis of particle titer and full rate of a recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) by SEC-UV-MALS-RI technique, which shares the application of SEC-MALS combined technology in quality control of rAAV products.
This column is established to raise the attention of the industry and research institutions to the quality of rAAV products, continuously improve the understanding of practitioners in rAAV product quality control, improve inspection and testing capabilities, and explore and establish corresponding experimental plans to promote the resolution of quality control problems, thereby promoting the construction of the quality control system and technical specifications for rAAV gene therapy products in China, and accelerating the high-quality development of gene therapy products.

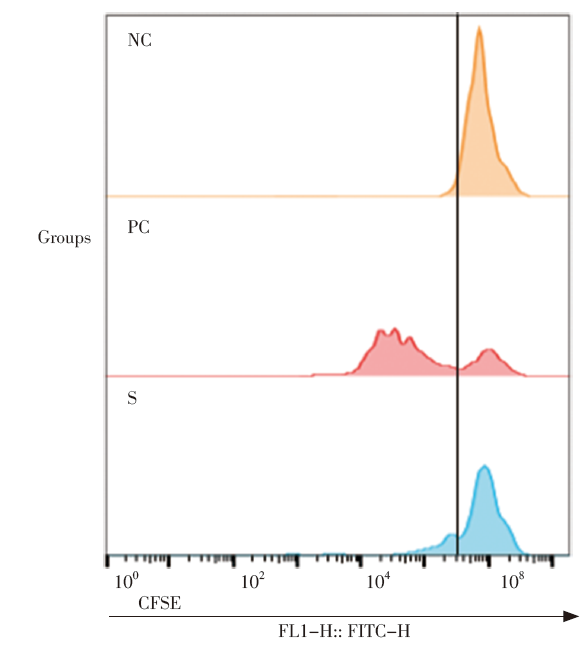
Bioassay (or biological method) is an important part for quality assessment in the production and marketing of biological products and other drugs. Validation of bioassay is an important scientific approach to ensure the accuracy and robustness of the test results and then ensure the reliability of the quality of biological products. Validation is one of the critical control points of the quality assurance system, and also the key audit content of various certifications and accreditations such as GMP and laboratory certification.
Bioassay which could be used to assess product quality was formed in the early 20th century. Throughout the 20th century, scientists from the fields of biology and statistics mainly focused on the research of application of this method, which was known as “bioactivity control method” in China, because of its many influencing factors, complicated operation and great variability of results.Since 2010, global methodological researchers in the pharmaceutical field had re-examined the validation contents of bioassay and physio-chemical methods according to the development and penetration of analytical quality by design (AQbD), life cycle, risk assessment and Six Sigma, and they transferred their research focus from application to the front end, such as the design, development and validation of bioassay. Thus, it could be truly started that the systematic methodology research stage of bioassay. For details, please refer to the “Overview of methodology research on bioassay” in this column.
10 papers contained in this column were the research summaries of more than 6 years, funded by the National Major New Drug Creation Project, Pharmacopoeia Projects, and the Quality Safety and Capability Building Project from NIFDC. In 2019, a phased summary column was published about part methodological research contents of physical and chemical methodsin the February issue of this magazine. The contents published in this issue are systematic research and innovative application based on extensive reference to the international research of bioassay.In this column, the process of historical development, the status quo of domestic and foreign regulation and guidelines and the latest research progress of bioassays are doing textual researched in the paper “Overview of methodology research on bioassay”. The definition and systematic classification of bioassays with the help of terminology theory was explored, and several expressions were discriminated about the name of bioassay in China, so as to help readers scientifically understand the essence of biological activity testing methods from a global perspective in the paper “Definition and taxonomy of biological method”. The most commonly used and easy confusing terms in bioassay studies were explained and compared in the paper “Analysis of key terms in bioassay”. Knowledges, which urgent needed for the establishment and evaluation of dose-effect model in the validation of bioassays, was focused on in the paper “Discussion on how to set up the dose-response model of bioassay”. The shortcomings in presentation of the values of biological potency were analyzed, and the integrity of presentation content in specification and daily report (including information about method suitability, the acceptance criterion and the significant figure of reportable value) and related calculation theory were systematically expound, in the two papers “Discussion on the scientific and standardized expression for reportable value of biological potency” and “Discussion on key points for setting up of the acceptance criteria of biological potency”. The experiment design to obtain accurate and reliable method performance parameters from the perspective of risk analysis and statistics was expounded and some common experimental design and thinking mode for design of method validation were provided in the paper “Discussion on the experiment design of bioassay validation”. The capability indexes which could describe the method capability were systematically summarized, including tolerance intervals and prediction interval of reported value, method capability index and method misjudgment rate, in the paper “Discussion on the evaluation indexes and criteria of assay for satisfying its intended use”. Some valuable application indexes of method that can be derived from the data set after method validated were mainly explored and summarized, including the format variability of method, the difference threshold of report value, the standard deviation for proficiency testing and the risk analysis of the key factors influencing the method, in the paper “Discussion on the application of method validation data set”. Finally, software named BMV 1.0 was introduced in the paper “Design and function of statistical software for validation of biological methods”, which was independently built by our laboratory to help experimenters solve the statistical analysis difficulties and get the indexes of method in the bioassay validation.
It is hoped that the publication of this column could provide systematic and comprehensive theoretical basis and statistical analysis support for peoples who worked in drug regulatory authorities, quality assessment laboratories and production enterprises in the evaluation of bioassay.
Ethnic medicine is an important part of Chinese traditional medicine, and has formed its own unique medical theoretical system. In the process of thousands of years of mutual integration, most of the ethnic groups have formed the development status of "pluralism, integration and difference". The population of ethnic minorities in China accounts for 6% of the total population, but their settlements account for 60% of the total area of the country. There are more than 8 000 kinds of ethnic medicinal materials in China, accounting for more than 70% of the total medicinal materials resources. They belong to the cultural system of more than 40 different nationalities, and have biological diversity and cultural diversity. There are more than 600 varieties of ethnic medicine, 47 of which were listed in the national basic medical insurance drug catalogue by the national labor and social security department in 2000.
In 2012, the Division of Chinese Materia Medica of National Institutes for Food and Drug Control (hereinafter referred to as "NIFDC") established the department of the ethnic medicine and set up a technical platform for the ethnic medicine in the national drug-control system which aimed to explore a new model suitable for the development of quality control of national drugs, and improve the quality inspection level of national drugs. This reflects the great importance attached to the quality research of ethnic drugs, and is of milestone significance to the development of ethnic drug testing. From 2013 to 2014, the NIFDC planned and organized a research project on ethnic medicine, which was supported by special funds from the Drug Registration Administration Department of the National Medicine Products Administration (hereinafter referred to as the "NMPA"). Since 2015, the NIFDC, as the leading unit, has jointly carried out research work with 13 national provincial (district) drug control institutes. With the support of the NMPA, three phases of project research have been carried out, the draft quality standards for 25 kinds of characteristic ethnic medicinal materials have been completed, and the research results have formed a compilation of conclusion reports of more than 1 000 000 words. Since June 2021, the project has added five strong provincial drug inspection units to carry out cooperative research, and carried out research on 32 ethnic drug varieties.
In order to strengthen the research of ethnic medicine, "Research for the Ethnic Medicine Column",including one comprehensive article and seven experimental article, has been specially set up in this issue. The paper—"Development and thinking of ethnic medicines based on patent analysis from 1994 to 2021" has analyzed the development status of ethnic medicine in China on the perspective of patent from 1994 to 2021. The results show that the ethnic medicine patent applications have experienced the embryonic stage from 1994 to 2003, the rapid development stage from 2003 to 2018 and the steady development stage from 2019 to now. It reflects that with the attention and support of the state to ethnic medicine and the efforts of scientific research institutions and scholars, some ethnic medicine work has made certain achievements. In the paper, "Identification of Polygoni Multiflori Radix, Dipsaci Radix, Morindae Officinalis Radix and Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma in Zishen Yutai pills by solid-phase extraction combined with thin layer chromatography", the standard improvement research was carried out on Zishen Yutai pills which containing 15 herbs contained in the drug standard of the Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, so as to lay a foundation for the follow-up study of ethnic medicine. In the paper, "Visualization analysis of spatial distribution of chemical compositions in Morindae Officinalis Radix processed product by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry imaging", the matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) has used to acquire the data of spatial distribution of iridoid and saccharous in Morindae Officinalis Radix and the contents of iridoid in the samples were determined by UPLC which provides a new way of thinking for the Chinese medicine processing. In the paper, "Research on improvement of quality standard of the Guangxi ethnic herb Onychii Herba", the quality standard and quality control level of Onychium japonicum (Thunb.) Kze. was improved. In the other four articles, "Comparison and optimization extraction of genomic DNA from Tibetan patent medicine Shiliu Jianwei powder", "Based on specific primer for the HRM identification method study of Tibetan patent medicine Shiliu Jianwei powder". "Genomic DNA extraction conditions optimization of Arnebiae Radix based on response surface methodology" and "RFLP-HRM identification method of Arnebiae Radix based on DNA barcoding and high resolution melting", DNA identification technology was used to optimize the extraction of genomic DNA from Arnebiae Radix and Shiliu Jianwei powder, so as to provide data support for the root cause of ethnic medicine.
Through the above research column, this issue hopes to provide readers with new ideas and new methods for the research of ethnic medicine, and expand the depth and breadth of ethnic medicine research, so as to promote the innovative development of ethnic medicine. And then to explore appropriate new models of ethnic medicine research, and jointly promote the development of basic research in the field of ethnic medicine.